Abstract
Background
Low cholesterol levels have been associated with an increased risk of haemorrhagic stroke. This study investigated whether lipid levels or prior statin use influence outcome in patients with acute ischaemic stroke treated with IV thrombolysis.
Methods
The relation between admission lipid levels or statin use and both the development of symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage (sICH) and 3-months functional outcome was assessed in a prospective hospital-based stroke registry comprising 252 patients treated with IV tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). The fasting status of the patients was unknown. Favourable outcome at 3 months was defined as a modified Rankin scale score ≤ 2. Logistic regression analysis was performed with adjustment for possible confounders.
Results
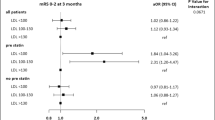
Low density lipoprotein (LDL), total cholesterol levels, and statin use were not associated with sICH. Mean triglyceride levels were significantly higher (2.5 mmol/L vs 1.8 mmol/L, p = 0.02) and high density lipoprotein (HDL) was significantly lower (1.0 mmol/L vs 1.2 mmol/L, p = 0.03) in patients with sICH than in patients without sICH. Multivariable analysis showed that higher triglyceride levels were independently associated with sICH (OR 2.16 per mmol/ L increase, 95 % CI 1.20–3.91, p = 0.01). There was no relation between any of the lipid levels or statin use and functional outcome at 3 months.
Conclusions
High admission triglyceride levels were independently associated with a higher risk of sICH, but were not associated with a reduced chance of a favourable functional outcome at 3 months. Total cholesterol levels, LDL levels and statin use had no influence on both the occurrence of sICH or functional outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. (1995) N Engl J Med 333(24):1581–1587
Intracerebral hemorrhage after intravenous t-PA therapy for ischemic stroke. The NINDS t-PA Stroke Study Group (1997) Stroke 28(11):2109–2118
Blood pressure, cholesterol, and stroke in eastern Asia. Eastern Stroke and Coronary Heart Disease Collaborative Research Group (1998) Lancet 352 (9143):1801–1807
Adams H, Adams R, del Zoppo G, Goldstein LB (2005) Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: 2005 guidelines update a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 36(4):916–923
Alvarez-Sabin J, Huertas R, Quintana M, Rubiera M, Delgado P, Ribo M, Molina CA, Montaner J (2007) Prior statin use may be associated with improved stroke outcome after tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 38(3):1076–1078
Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina CA, Montaner J, Arenillas JF, Huertas R, Ribo M, Codina A, Quintana M (2003) Effects of admission hyperglycemia on stroke outcome in reperfused tissue plasminogen activator-treated patients. Stroke 34(5):1235–1240
Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A, III, Goldstein LB, Hennerici M, Rudolph AE, Sillesen H, Simunovic L, Szarek M, Welch KM, Zivin JA (2006) High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med 355(6):549–559
Ariesen MJ, Claus SP, Rinkel GJ, Algra A (2003) Risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage in the general population: a systematic review. Stroke 34(8):2060–2065
Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Warlow C, Burn J (1991) Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 337(8756):1521–1526
Bang OY, Saver JL, Liebeskind DS, Starkman S, Villablanca P, Salamon N, Buck B, Ali L, Restrepo L, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Razinia T, Ovbiagele B (2007) Cholesterol level and symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke thrombolysis. Neurology 68(10):737–742
Butterworth RJ, Marshall WJ, Bath PMW (1997) Changes in Serum Lipid Measurements following Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 7:10–13
Castellanos M, Leira R, Serena J, Pumar JM, Lizasoain I, Castillo J, Davalos A (2003) Plasma metalloproteinase-9 concentration predicts hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34(1):40–46
Demchuk AM, Tanne D, Hill MD, Kasner SE, Hanson S, Grond M, Levine SR (2001) Predictors of good outcome after intravenous tPA for acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 57(3):474–480
Ebrahim S, Sung J, Song YM, Ferrer RL, Lawlor DA, Davey SG (2006) Serum cholesterol, haemorrhagic stroke, ischaemic stroke, and myocardial infarction: Korean national health system prospective cohort study. BMJ 333(7557):22
Ferreira AC, Peter AA, Mendez AJ, Jimenez JJ, Mauro LM, Chirinos JA, Ghany R, Virani S, Garcia S, Horstman LL, Purow J, Jy W, Ahn YS, de ME (2004) Postprandial hypertriglyceridemia increases circulating levels of endothelial cell microparticles. Circulation 110(23):3599–3603
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, Larrue V, Bluhmki E, Davis S, Donnan G (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Lancet 352(9136):1245–1251
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Hazuda HP, Mitchell BD, Patterson JK (1990) Cardiovascular risk factors in confirmed prediabetic individuals. Does the clock for coronary heart disease start ticking before the onset of clinical diabetes? JAMA 263(21):2893–2898
Heuschmann PU, Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Roether J, Misselwitz B, Lowitzsch K, Heidrich J, Hermanek P, Leffmann C, Sitzer M, Biegler M, Buecker-Nott HJ, Berger K (2004) Predictors of inhospital mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with thrombolytic therapy. JAMA 292(15):1831–1838
Lapchak PA, Chapman DF, Zivin JA (2000) Metalloproteinase inhibition reduces thrombolytic (tissue plasminogen activator)-induced hemorrhage after thromboembolic stroke. Stroke 31(12):3034–3040
Montaner J, Molina CA, Monasterio J, Abilleira S, Arenillas JF, Ribo M, Quintana M, Alvarez-Sabin J (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 pretreatment level predicts intracranial hemorrhagic complications after thrombolysis in human stroke. Circulation 107(4):598–603
Paciaroni M, Agnelli G, Caso V, Venti M, Alberti A, Milia P, Silvestrelli G, Biagini S (2006) Prior use of antithrombotic agents and neurological functional outcome at discharge in patients with ischemic stroke. J Thromb Haemost 4(9):1957–1961
Parsons MW, Barber PA, Desmond PM, Baird TA, Darby DG, Byrnes G, Tress BM, Davis SM (2002) Acute hyperglycemia adversely affects stroke outcome: a magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy study. Ann Neurol 52(1):20–28
Tanne D, Kasner SE, Demchuk AM, Koren-Morag N, Hanson S, Grond M, Levine SR (2002) Markers of increased risk of intracerebral hemorrhage after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator therapy for acute ischemic stroke in clinical practice. The multicenter rt-PA acute stroke survey. Circulation 105(14):1679–1685
Tirschwell DL, Smith NL, Heckbert SR, Lemaitre RN, Longstreth WT Jr, Psaty BM (2004) Association of cholesterol with stroke risk varies in stroke subtypes and patient subgroups. Neurology 63(10):1868–1875
Uyttenboogaart M, Koch MW, Stewart RE, Vroomen PC, Luijckx GJ, De Keyser J (2007) Moderate hyperglycaemia is associated with favourable outcome in acute lacunar stroke. Brain 130(Pt 6):1626–1630
Uyttenboogaart M, Vroomen PC, Stewart RE, De Keyser J, Luijckx GJ (2007) Safety of routine IV thrombolysis between 3 and 4. 5 h after ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 254(1–2):28–32
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19(5):604–607
Wang S, Lee SR, Guo SZ, Kim WJ, Montaner J, Wang X, Lo EH (2006) Reduction of tissue plasminogen activator-induced matrix metalloproteinase- 9 by simvastatin in astrocytes. Stroke 37(7):1910–1912
Wardlaw JM, del Zoppo G, Yamaguchi T, Berge E (2003) Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev(3):CD000213
Zia E, Pessah-Rasmussen H, Khan FA, Norrving B, Janzon L, Berglund G, Engstrom G (2006) Risk factors for primary intracerebral hemorrhage: a population-based nested case-control study. Cerebrovasc Dis 21(1–2):18–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We declare we have no conflicts of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uyttenboogaart, M., Koch, M.W., Koopman, K. et al. Lipid profile, statin use, and outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol 255, 875–880 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0797-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0797-7