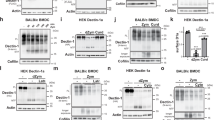
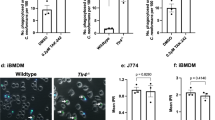
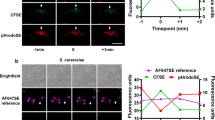
Abstract
Macrophages orchestrate innate immunity by phagocytosing pathogens and coordinating inflammatory responses1. Effective defence requires the host to discriminate between different pathogens. The specificity of innate immune recognition in Drosophila is mediated by the Toll family of receptors2,3; Toll mediates anti-fungal responses, whereas 18-wheeler mediates anti-bacterial defence4,5,6. A large number of Toll homologues have been identified in mammals, and Toll-like receptor 4 is critical in responses to Gram-negative bacteria7,8,9,10,11. Here we show that Toll-like receptor 2 is recruited specifically to macrophage phagosomes containing yeast, and that a point mutation in the receptor abrogates inflammatory responses to yeast and Gram-positive bacteria, but not to Gram-negative bacteria. Thus, during the phagocytosis of pathogens, two classes of innate immune receptors cooperate to mediate host defence: phagocytic receptors, such as the mannose receptor, signal particle internalization, and the Toll-like receptors sample the contents of the vacuole and trigger an inflammatory response appropriate to defence against the specific organism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderem,A. & Underhill,D. M. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 593–623 (1999).
Medzhitov,R. & Janeway,C. A. Jr Self-defence: the fruit fly style. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 429–430 (1998).
Hoffmann,J. A., Kafatos,F. C., Janeway,C. A. & Ezekowitz,R. A. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 284, 1313–1318 (1999).
Lemaitre,B., Reichhart,J. M. & Hoffmann,J. A. Drosophila host defense: differential induction of antimicrobial peptide genes after infection by various classes of microorganisms. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14614–14619 (1997).
Eldon,E. et al. The Drosophila 18 wheeler is required for morphogenesis and has striking similarities to Toll. Development 120, 885–899 (1994).
Williams,M. J., Rodriguez,A., Kimbrell,D. A. & Eldon,E. D. The 18-wheeler mutation reveals complex antibacterial gene regulation in Drosophila host defense. EMBO J. 16, 6120–6130 (1997).
Chaudhary,P. M. et al. Cloning and characterization of two Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor-like genes TIL3 and TIL4: evidence for a multi-gene receptor family in humans. Blood 91, 4020–4027 (1998).
Rock,F. L., Hardiman,G., Timans,J. C., Kastelein,R. A. & Bazan,J. F. A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 588–593 (1998).
Takeuchi,O. et al. TLR6: a novel member of an expanding Toll-like receptor family. Gene 231, 59–65 (1999).
Poltorak,A et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in TIr4 gene. Science 282, 2085–2088 (1998).
Qureshi,S. T. et al. Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4). J. Exp. Med. 189, 615–625 (1999).
Stahl,P. D. & Ezekowitz,R. A. The mannose receptor is a pattern recognition receptor involved in host defense. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 10, 50–55 (1998).
Hoshino,K. et al. Cutting edge: toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J. Immunol. 162, 3749–3752 (1999).
Heine,H. et al. Cutting edge: cells that carry A null allele for toll-like receptor 2 are capable of responding to endotoxin. J. Immunol. 162, 6971–6975 (1999).
Yoshimura,A. et al. Cutting edge: recognition of Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via toll-like receptor 2. J. Immunol. 163, 1–5 (1999).
Schwandner,R., Dziarski,R., Wesche,H., Rothe,M. & Kirschning,C. J. Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17406–17409 (1999).
Medzhitov,R. et al. MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. 2, 253–258 (1998).
Muzio,M., Ni,J., Feng,P. & Dixit,V. M. IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signalling. Science 278, 1612–1615 (1997).
Wesche,H., Henzel,W. J., Schillinglaw,W., Li,S. & Cao,Z. MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 7, 837–847 (1997).
Adachi,O. et al. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 9, 143–150 (1998).
Freudenberg,M. A. & Galanos,C. Tumor necrosis factor α mediates lethal activity of killed gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria in D-galactosamine-treated mice. Infect. Immun. 59, 2110–2115 (1991).
Kirschning,C. J., Wesche,H., Merrill Ayres,T. & Rothe,M. Human toll-like receptor 2 confers responsiveness to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 188, 2091–2097 (1998).
Yang,R. B. et al. Toll-like receptor-2 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular signalling. Nature 395, 284–288 (1998).
Gossen,M. & Bujard,H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5547–5551 (1992).
Underhill,D. M., Chen,J., Allen,L. A. & Aderem,A. MacMARCKS is not essential for phagocytosis in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33619–33623 (1998).
Schindler,U. & Baichwal,V. R. Three NF-κB binding sites in the human E-selectin gene required for maximal tumor necrosis factor α-induced expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 5820–5831 (1994).
Sweetser,M. T. et al. The roles of nuclear factor of activated T cells and ying-yang 1 in activation-induced expression of the interferon-γ promoter in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 34775–34783 (1998).
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by grants from the NIH (A.A., C.B.W. and A.S.) and from the cystic fibrosis foundation (C.B.W. and A.H.). D.M.U. is an Irvington Institute postdoctoral fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Underhill, D., Ozinsky, A., Hajjar, A. et al. The Toll-like receptor 2 is recruited to macrophage phagosomes and discriminates between pathogens. Nature 401, 811–815 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/44605
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/44605
This article is cited by
-
Dectin-1 ligands produce distinct training phenotypes in human monocytes through differential activation of signaling networks
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Hepatic stellate cell activation markers are regulated by the vagus nerve in systemic inflammation
Bioelectronic Medicine (2023)
-
Mutant huntingtin confers cell-autonomous phenotypes on Huntington’s disease iPSC-derived microglia
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Receptor basis of biological activity of polysaccharides
Biophysical Reviews (2023)
-
Immunomodulatory Effect of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Streptococcus Strains of Paraprobiotics in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses in RAW-264.7 Macrophages
Current Microbiology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.