Abstract
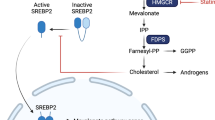
The mevalonate pathway is a core biochemical process, crucial for the generation of cholesterol and other key metabolic end products. The rate-limiting enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), is safely and effectively targeted by the statin family of inhibitors to treat hypercholesterolemia. The anticancer activity of statins has also been widely reported, yet the tumor-selective mechanisms that mediate these antiproliferative effects remain largely unclear. The importance of altered metabolism in the context of tumorigenesis has received renewed attention as metabolic changes entwined with the molecular hallmarks of cancer have been elucidated. Although several metabolic pathways have been linked to cancer progression and etiology, it was only recently that HMGCR and the mevalonate pathway were also shown to have a distinct role in cellular transformation. In this review, we chart the historical progression of statins from cholesterol-lowering blockbusters to anticancer agents with imminent potential, and further discuss an emerging role for HMGCR and the mevalonate pathway in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldstein JL, Brown MS . Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 1990; 343: 425–430.
Endo A . The discovery and development of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Lipid Res 1992; 33: 1569–1582.
Wong WW, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD, Penn LZ . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis. Leukemia 2002; 16: 508–519.
Steinberg D, Gotto Jr AM . Preventing coronary artery disease by lowering cholesterol levels: fifty years from bench to bedside. Jama 1999; 282: 2043–2050.
Tobert JA . Lovastatin and beyond: the history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003; 2: 517–526.
Kannel WB . Clinical misconceptions dispelled by epidemiological research. Circulation 1995; 92: 3350–3360.
NIH Consensus Development Conference. Lowering blood cholesterol to prevent heart disease. Wis Med J 1985; 84: 18–19.
Endo A, Kuroda M, Tanzawa K . Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett 1976; 72: 323–326.
Kaneko I, Hazama-Shimada Y, Endo A . Inhibitory effects on lipid metabolism in cultured cells of ML-236B, a potent inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase. Eur J Biochem 1978; 87: 313–321.
Tsujita Y, Kuroda M, Tanzawa K, Kitano N, Endo A . Hypolipidemic effects in dogs of ML-236B, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Atherosclerosis 1979; 32: 307–313.
Yamamoto A, Sudo H, Endo A . Therapeutic effects of ML-236B in primary hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 1980; 35: 259–266.
Grundy SM . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors for treatment of hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 1988; 319: 24–33.
MAAS Investigators. Effect of simvastatin on coronary atheroma: the Multicentre Anti-Atheroma Study (MAAS). Lancet 1994; 344: 633–638.
Blankenhorn DH, Azen SP, Kramsch DM, Mack WJ, Cashin-Hemphill L, Hodis HN et al. Coronary angiographic changes with lovastatin therapy. The Monitored Atherosclerosis Regression Study (MARS). Ann Intern Med 1993; 119: 969–976.
Furberg CD, Adams Jr HP, Applegate WB, Byington RP, Espeland MA, Hartwell T et al. Effect of lovastatin on early carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events. Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Progression Study (ACAPS) Research Group. Circulation 1994; 90: 1679–1687.
Jukema JW, Bruschke AV, van Boven AJ, Reiber JH, Bal ET, Zwinderman AH et al. Effects of lipid lowering by pravastatin on progression and regression of coronary artery disease in symptomatic men with normal to moderately elevated serum cholesterol levels. The Regression Growth Evaluation Statin Study (REGRESS). Circulation 1995; 91: 2528–2540.
Pitt B, Mancini GB, Ellis SG, Rosman HS, Park JS, McGovern ME . Pravastatin limitation of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries (PLAC I): reduction in atherosclerosis progression and clinical events. PLAC I investigation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995; 26: 1133–1139.
Salonen R, Nyyssonen K, Porkkala E, Rummukainen J, Belder R, Park JS et al. Kuopio Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (KAPS). A population-based primary preventive trial of the effect of LDL lowering on atherosclerotic progression in carotid and femoral arteries. Circulation 1995; 92: 1758–1764.
Waters D, Higginson L, Gladstone P, Kimball B, Le May M, Boccuzzi SJ et al. Effects of monotherapy with an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis as assessed by serial quantitative arteriography. The Canadian Coronary Atherosclerosis Intervention Trial. Circulation 1994; 89: 959–968.
Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994; 344: 1383–1389.
Pedersen TR, Berg K, Cook TJ, Faergeman O, Haghfelt T, Kjekshus J et al. Safety and tolerability of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin during 5 years in the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study. Arch Intern Med 1996; 156: 2085–2092.
The Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1349–1357.
Downs JR, Clearfield M, Weis S, Whitney E, Shapiro DR, Beere PA et al. Primary prevention of acute coronary events with lovastatin in men and women with average cholesterol levels: results of AFCAPS/TexCAPS. Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study. Jama 1998; 279: 1615–1622.
Sacks FM, Pfeffer MA, Moye LA, Rouleau JL, Rutherford JD, Cole TG et al. The effect of pravastatin on coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. Cholesterol and Recurrent Events Trial investigators. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 1001–1009.
Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I, Isles CG, Lorimer AR, MacFarlane PW et al. Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia. West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1301–1307.
Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2002; 360: 7–22.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL . The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 1997; 89: 331–340.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL . Cholesterol feedback: from Schoenheimer's bottle to Scap's MELADL. J Lipid Res 2009; 50 (Suppl): S15–S27.
Davidson MH . Safety profiles for the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors: treatment and trust. Drugs 2001; 61: 197–206.
Pocathikorn A, Taylor RR, Mamotte CD . Atorvastatin increases expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor mRNA in human circulating mononuclear cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2010; 37: 471–476.
Keyomarsi K, Sandoval L, Band V, Pardee AB . Synchronization of tumor and normal cells from G1 to multiple cell cycles by lovastatin. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 3602–3609.
Jakobisiak M, Bruno S, Skierski JS, Darzynkiewicz Z . Cell cycle-specific effects of lovastatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 3628–3632.
Gray-Bablin J, Rao S, Keyomarsi K . Lovastatin induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in human breast cells occurs in a cell cycle-independent fashion. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 604–609.
Wachtershauser A, Akoglu B, Stein J . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor mevastatin enhances the growth inhibitory effect of butyrate in the colorectal carcinoma cell line Caco-2. Carcinogenesis 2001; 22: 1061–1067.
Rao S, Lowe M, Herliczek TW, Keyomarsi K . Lovastatin mediated G1 arrest in normal and tumor breast cells is through inhibition of CDK2 activity and redistribution of p21 and p27, independent of p53. Oncogene 1998; 17: 2393–2402.
Wong WW, Clendening JW, Martirosyan A, Boutros PC, Bros C, Khosravi F et al. Determinants of sensitivity to lovastatin-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther 2007; 6: 1886–1897.
Newman A, Clutterbuck RD, Powles RL, Catovsky D, Millar JL . A comparison of the effect of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors simvastatin, lovastatin and pravastatin on leukaemic and normal bone marrow progenitors. Leuk Lymphoma 1997; 24: 533–537.
Dimitroulakos J, Nohynek D, Backway KL, Hedley DW, Yeger H, Freedman MH et al. Increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemias to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: A potential therapeutic approach. Blood 1999; 93: 1308–1318.
Clendening JW, Pandyra A, Li Z, Boutros PC, Martirosyan A, Lehner R et al. Exploiting the mevalonate pathway to distinguish statin-sensitive multiple myeloma. Blood 2010; 115: 4787–4797.
Dimitroulakos J, Ye LY, Benzaquen M, Moore MJ, Kamel-Reid S, Freedman MH et al. Differential sensitivity of various pediatric cancers and squamous cell carcinomas to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 158–167.
Perez-Sala D, Mollinedo F . Inhibition of isoprenoid biosynthesis induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994; 199: 1209–1215.
Newman A, Clutterbuck RD, Powles RL, Millar JL . Selective inhibition of primary acute myeloid leukaemia cell growth by simvastatin. Leukemia 1994; 8: 2023–2029.
Macaulay RJ, Wang W, Dimitroulakos J, Becker LE, Yeger H . Lovastatin-induced apoptosis of human medulloblastoma cell lines in vitro. J Neurooncol 1999; 42: 1–11.
Rubins JB, Greatens T, Kratzke RA, Tan AT, Polunovsky VA, Bitterman P . Lovastatin induces apoptosis in malignant mesothelioma cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 1616–1622.
Muller C, Bockhorn AG, Klusmeier S, Kiehl M, Roeder C, Kalthoff H et al. Lovastatin inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cell lines with mutant as well as with wild-type K-ras oncogene but has different effects on protein phosphorylation and induction of apoptosis. Int J Oncol 1998; 12: 717–723.
Dimitroulakos J, Yeger H . HMG-CoA reductase mediates the biological effects of retinoic acid on human neuroblastoma cells: lovastatin specifically targets P-glycoprotein-expressing cells. Nat Med 1996; 2: 326–333.
Jones KD, Couldwell WT, Hinton DR, Su Y, He S, Anker L et al. Lovastatin induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human malignant glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994; 205: 1681–1687.
van de Donk NW, Kamphuis MM, Lokhorst HM, Bloem AC . The cholesterol lowering drug lovastatin induces cell death in myeloma plasma cells. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1362–1371.
Otsuki T, Sakaguchi H, Hatayama T, Fujii T, Tsujioka T, Sugihara T et al. Effects of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin, on human myeloma cells. Oncol Rep 2004; 11: 1053–1058.
Gronich N, Drucker L, Shapiro H, Radnay J, Yarkoni S, Lishner M . Simvastatin induces death of multiple myeloma cell lines. J Investig Med 2004; 52: 335–344.
Morgan MA, Sebil T, Aydilek E, Peest D, Ganser A, Reuter CW . Combining prenylation inhibitors causes synergistic cytotoxicity, apoptosis and disruption of RAS-to-MAP kinase signalling in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Haematol 2005; 130: 912–925.
Fritz G . Targeting the mevalonate pathway for improved anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2009; 9: 626–638.
Jakobisiak M, Golab J . Statins can modulate effectiveness of antitumor therapeutic modalities. Med Res Rev 2010; 30: 102–135.
Sassano A, Platanias LC . Statins in tumor suppression. Cancer Lett 2008; 260: 11–19.
Holstein SA, Knapp HR, Clamon GH, Murry DJ, Hohl RJ . Pharmacodynamic effects of high dose lovastatin in subjects with advanced malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2006; 57: 155–164.
Kawata S, Yamasaki E, Nagase T, Inui Y, Ito N, Matsuda Y et al. Effect of pravastatin on survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled trial. Br J Cancer 2001; 84: 886–891.
Kornblau SM, Banker DE, Stirewalt D, Shen D, Lemker E, Verstovsek S et al. Blockade of adaptive defensive changes in cholesterol uptake and synthesis in AML by the addition of pravastatin to idarubicin + high-dose Ara-C: a phase 1 study. Blood 2007; 109: 2999–3006.
Lopez-Aguilar E, Sepulveda-Vildosola AC, Rivera-Marquez H, Cerecedo-Diaz F, Valdez-Sanchez M, Villasis-Keever MA . Security and maximal tolerated doses of fluvastatin in pediatric cancer patients. Arch Med Res 1999; 30: 128–131.
Thibault A, Samid D, Tompkins AC, Figg WD, Cooper MR, Hohl RJ et al. Phase I study of lovastatin, an inhibitor of the mevalonate pathway, in patients with cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 483–491.
van der Spek E, Bloem AC, van de Donk NW, Bogers LH, van der Griend R, Kramer MH et al. Dose-finding study of high-dose simvastatin combined with standard chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma or lymphoma. Haematologica 2006; 91: 542–545.
Garwood ER, Kumar AS, Baehner FL, Moore DH, Au A, Hylton N et al. Fluvastatin reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis in women with high grade breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010; 119: 137–144.
Schmidmaier R, Baumann P, Bumeder I, Meinhardt G, Straka C, Emmerich B . First clinical experience with simvastatin to overcome drug resistance in refractory multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol 2007; 79: 240–243.
Knox JJ, Siu LL, Chen E, Dimitroulakos J, Kamel-Reid S, Moore MJ et al. A Phase I trial of prolonged administration of lovastatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck or of the cervix. Eur J Cancer 2005; 41: 523–530.
Larner J, Jane J, Laws E, Packer R, Myers C, Shaffrey M . A phase I-II trial of lovastatin for anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Clin Oncol 1998; 21: 579–583.
van der Spek E, Bloem AC, Sinnige HA, Lokhorst HM . High dose simvastatin does not reverse resistance to vincristine, adriamycin, and dexamethasone (VAD) in myeloma. Haematologica 2007; 92: e130–e131.
Kim WS, Kim MM, Choi HJ, Yoon SS, Lee MH, Park K et al. Phase II study of high-dose lovastatin in patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Invest New Drugs 2001; 19: 81–83.
Lersch C, Schmelz R, Erdmann J, Hollweck R, Schulte-Frohlinde E, Eckel F et al. Treatment of HCC with pravastatin, octreotide, or gemcitabine--a critical evaluation. Hepatogastroenterology 2004; 51: 1099–1103.
Konings IR, van der Gaast A, van der Wijk LJ, de Jongh FE, Eskens FA, Sleijfer S . The addition of pravastatin to chemotherapy in advanced gastric carcinoma: a randomised phase II trial. Eur J Cancer 2010; 46: 3200–3204.
Graf H, Jungst C, Straub G, Dogan S, Hoffmann RT, Jakobs T et al. Chemoembolization combined with pravastatin improves survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion 2008; 78: 34–38.
Lopez-Aguilar E, Sepulveda-Vildosola AC, Betanzos-Cabrera Y, Rocha-Moreno YG, Gascon-Lastiri G, Rivera-Marquez H et al. Phase II study of metronomic chemotherapy with thalidomide, carboplatin-vincristine-fluvastatin in the treatment of brain stem tumors in children. Arch Med Res 2008; 39: 655–662.
Lee J, Jung KH, Park YS, Ahn JB, Shin SJ, Im SA et al. Simvastatin plus irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFIRI) as first-line chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal patients: a multicenter phase II study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009; 64: 657–663.
Sondergaard TE, Pedersen PT, Andersen TL, Soe K, Lund T, Ostergaard B et al. A phase II clinical trial does not show that high dose simvastatin has beneficial effect on markers of bone turnover in multiple myeloma. Hematol Oncol 2009; 27: 17–22.
Minden MD, Dimitroulakos J, Nohynek D, Penn LZ . Lovastatin induced control of blast cell growth in an elderly patient with acute myeloblastic leukemia. Leukemia Lymphoma 2000; 40: 659–662.
Cauley JA, McTiernan A, Rodabough RJ, LaCroix A, Bauer DC, Margolis KL et al. Statin use and breast cancer: prospective results from the Women's Health Initiative. J Natl Cancer Inst 2006; 98: 700–707.
El-Serag HB, Johnson ML, Hachem C, Morgana RO . Statins are associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a large cohort of patients with diabetes. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 1601–1608.
Graaf MR, Beiderbeck AB, Egberts AC, Richel DJ, Guchelaar HJ . The risk of cancer in users of statins. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2388–2394.
Dale KM, Coleman CI, Henyan NN, Kluger J, White CM . Statins and cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Jama 2006; 295: 74–80.
Kuoppala J, Lamminpaa A, Pukkala E . Statins and cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 2008; 44: 2122–2132.
Poynter JN, Gruber SB, Higgins PD, Almog R, Bonner JD, Rennert HS et al. Statins and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2184–2192.
Kumar AS, Benz CC, Shim V, Minami CA, Moore DH, Esserman LJ . Estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer is less likely to arise among lipophilic statin users. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008; 17: 1028–1033.
Kwan ML, Habel LA, Flick ED, Quesenberry CP, Caan B . Post-diagnosis statin use and breast cancer recurrence in a prospective cohort study of early stage breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008; 109: 573–579.
Ahern TP, Pedersen L, Tarp M, Cronin-Fenton DP, Garne JP, Silliman RA et al. Statin prescriptions and breast cancer recurrence risk: a Danish Nationwide Prospective Cohort Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011; 103: 1461–1468.
Bonovas S, Filioussi K, Tsavaris N, Sitaras NM . Use of statins and breast cancer: a meta-analysis of seven randomized clinical trials and nine observational studies. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 8606–8612.
Boudreau DM, Yu O, Miglioretti DL, Buist DS, Heckbert SR, Daling JR . Statin use and breast cancer risk in a large population-based setting. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007; 16: 416–421.
Woditschka S, Habel LA, Udaltsova N, Friedman GD, Sieh W . Lipophilic statin use and risk of breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 19: 2479–2487.
Moorman PG, Hamilton RJ . Statins and cancer risk: what do we know and where do we go from here? Epidemiology 2007; 18: 194–196.
Taylor ML, Wells BJ, Smolak MJ . Statins and cancer: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Eur J Cancer Prev 2008; 17: 259–268.
Tan N, Klein EA, Li J, Moussa AS, Jones JS . Statin use and risk of prostate cancer in a population of men who underwent biopsy. J Urol 2011; 186: 86–90.
Boudreau DM, Yu O, Johnson J . Statin use and cancer risk: a comprehensive review. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2010; 9: 603–621.
Cernuda-Morollon E, Ridley AJ . Rho GTPases and leukocyte adhesion receptor expression and function in endothelial cells. Circ Res 2006; 98: 757–767.
Forrester JS, Libby P . The inflammation hypothesis and its potential relevance to statin therapy. Am J Cardiol 2007; 99: 732–738.
Fildes JE, Shaw SM, Williams SG, Yonan N . Potential immunologic effects of statins in cancer following transplantation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2009; 58: 461–467.
Samson KT, Minoguchi K, Tanaka A, Oda N, Yokoe T, Okada S et al. Effect of fluvastatin on apoptosis in human CD4+ T cells. Cell Immunol 2005; 235: 136–144.
Nabatov AA, Pollakis G, Linnemann T, Paxton WA, de Baar MP . Statins disrupt CCR5 and RANTES expression levels in CD4(+) T lymphocytes in vitro and preferentially decrease infection of R5 versus X4 HIV-1. PLoS One 2007; 2: e470.
Veillard NR, Braunersreuther V, Arnaud C, Burger F, Pelli G, Steffens S et al. Simvastatin modulates chemokine and chemokine receptor expression by geranylgeranyl isoprenoid pathway in human endothelial cells and macrophages. Atherosclerosis 2006; 188: 51–58.
Guan JZ, Murakami H, Yamato K, Tanabe J, Matsui J, Tamasawa N et al. Effects of fluvastatin in type 2 diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia: reduction in cholesterol oxidation products and VCAM-1. J Atheroscler Thromb 2004; 11: 56–61.
Landsberger M, Wolff B, Jantzen F, Rosenstengel C, Vogelgesang D, Staudt A et al. Cerivastatin reduces cytokine-induced surface expression of ICAM-1 via increased shedding in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2007; 190: 43–52.
Cox G, O’Byrne KJ . Matrix metalloproteinases and cancer. Anticancer Res 2001; 21: 4207–4219.
Cutts JL, Scallen TJ, Watson J, Bankhurst AD . Role of mevalonic acid in the regulation of natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Cell Physiol 1989; 139: 550–557.
Tanaka T, Porter CM, Horvath-Arcidiacono JA, Bloom ET . Lipophilic statins suppress cytotoxicity by freshly isolated natural killer cells through modulation of granule exocytosis. Int Immunol 2007; 19: 163–173.
Dirks AJ, Jones KM . Statin-induced apoptosis and skeletal myopathy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006; 291: C1208–C1212.
Lamperti C, Naini AB, Lucchini V, Prelle A, Bresolin N, Moggio M et al. Muscle coenzyme Q10 level in statin-related myopathy. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 1709–1712.
Clendening JW, Pandyra A, Boutros PC, El Ghamrasni S, Khosravi F, Trentin GA et al. Dysregulation of the mevalonate pathway promotes transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 15051–15056.
Banker DE, Mayer SJ, Li HY, Willman CL, Appelbaum FR, Zager RA . Cholesterol synthesis and import contribute to protective cholesterol increments in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2004; 104: 1816–1824.
Li HY, Appelbaum FR, Willman CL, Zager RA, Banker DE . Cholesterol-modulating agents kill acute myeloid leukemia cells and sensitize them to therapeutics by blocking adaptive cholesterol responses. Blood 2003; 101: 3628–3634.
Siperstein MD . Cholesterol and cancer. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 1970; 81: 107–118.
Buchwald H . Cholesterol inhibition, cancer, and chemotherapy. Lancet 1992; 339: 1154–1156.
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Joshi A, Zhang Y, Jaeger SA, Bulyk M et al. A transcriptional signature and common gene networks link cancer with lipid metabolism and diverse human diseases. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 348–361.
Lucken-Ardjomande S, Montessuit S, Martinou JC . Bax activation and stress-induced apoptosis delayed by the accumulation of cholesterol in mitochondrial membranes. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 484–493.
Kok DE, van Roermund JG, Aben KK, den Heijer M, Swinkels DW, Kampman E et al. Blood lipid levels and prostate cancer risk; a cohort study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2011; 14: 340–345.
Hu J, La Vecchia C, de Groh M, Negri E, Morrison H, Mery L . Dietary cholesterol intake and cancer. Ann Oncol 2011 (e-pub ahead of print 4 May 2011).
Chao FC, Efron B, Wolf P . The possible prognostic usefulness of assessing serum proteins and cholesterol in malignancy. Cancer 1975; 35: 1223–1229.
Mo H, Elson CE . Studies of the isoprenoid-mediated inhibition of mevalonate synthesis applied to cancer chemotherapy and chemoprevention. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004; 229: 567–585.
Larsson O . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: role in normal and malignant cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1996; 22: 197–212.
Farmer P, Bonnefoi H, Becette V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Fumoleau P, Larsimont D et al. Identification of molecular apocrine breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4660–4671.
Celis JE, Gromov P, Moreira JM, Cabezon T, Friis E, Vejborg IM et al. Apocrine cysts of the breast: biomarkers, origin, enlargement, and relation with cancer phenotype. Mol Cell Proteomics 2006; 5: 462–483.
Duncan RE, El-Sohemy A, Archer MC . Delivery of mevalonate to murine extrahepatic tissues via mini-osmotic pumps. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 2004; 50: 139–143.
Cao Z, Fan-Minogue H, Bellovin DI, Yevtodiyenko A, Arzeno J, Yang Q et al. MYC Phosphorylation, Activation, and Tumorigenic Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma are Regulated by HMG-CoA Reductase. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 2286–2297.
Warburg O . On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956; 123: 309–314.
Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J . Tumor cell metabolism: cancer's Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 472–482.
Pan JG, Mak TW . Metabolic targeting as an anticancer strategy: dawn of a new era? Sci STKE 2007; 2007: pe14.
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB . The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 2008; 7: 11–20.
Kim JW, Dang CV . Cancer's molecular sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 8927–8930.
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW . Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 85–95.
Bauer DE, Hatzivassiliou G, Zhao F, Andreadis C, Thompson CB . ATP citrate lyase is an important component of cell growth and transformation. Oncogene 2005; 24: 6314–6322.
Janardhan S, Srivani P, Sastry GN . Choline kinase: an important target for cancer. Curr Med Chem 2006; 13: 1169–1186.
Migita T, Ruiz S, Fornari A, Fiorentino M, Priolo C, Zadra G et al. Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic enzyme and candidate oncogene in prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009; 101: 519–532.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Altenberg B, Greulich KO . Genes of glycolysis are ubiquitously overexpressed in 24 cancer classes. Genomics 2004; 84: 1014–1020.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Pallottini V, Guantario B, Martini C, Totta P, Filippi I, Carraro F et al. Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase expression by hypoxia. J Cell Biochem 2008; 104: 701–709.
Porstmann T, Santos CR, Griffiths B, Cully M, Wu M, Leevers S et al. SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metab 2008; 8: 224–236.
Yuan TL, Cantley LC . PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5497–5510.
Kuhajda FP . AMP-activated protein kinase and human cancer: cancer metabolism revisited. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32 (Suppl 4): S36–S41.
Motoshima H, Goldstein BJ, Igata M, Araki E . AMPK and cell proliferation--AMPK as a therapeutic target for atherosclerosis and cancer. J Physiol 2006; 574: 63–71.
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X, Jiang B et al. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 2011; 13: 376–388.
Zhang FL, Casey PJ . Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu Rev Biochem 1996; 65: 241–269.
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV, Papavassiliou AG . Post-translational modifications and regulation of the RAS superfamily of GTPases as anticancer targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007; 6: 541–555.
Yun J, Rago C, Cheong I, Pagliarini R, Angenendt P, Rajagopalan H et al. Glucose deprivation contributes to the development of KRAS pathway mutations in tumor cells. Science 2009; 325: 1555–1559.
Ramanathan A, Wang C, Schreiber SL . Perturbational profiling of a cell-line model of tumorigenesis by using metabolic measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 5992–5997.
Kikuchi H, Pino MS, Zeng M, Shirasawa S, Chung DC . Oncogenic KRAS and BRAF differentially regulate hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in colon cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8499–8506.
Sears R, Leone G, DeGregori J, Nevins JR . Ras enhances Myc protein stability. Mol Cell 1999; 3: 169–179.
Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F, Maity A . Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 9519–9525.
Huang J, Manning BD . The TSC1-TSC2 complex: a molecular switchboard controlling cell growth. Biochem J 2008; 412: 179–190.
Sancak Y, Thoreen CC, Peterson TR, Lindquist RA, Kang SA, Spooner E et al. PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol Cell 2007; 25: 903–915.
Menon S, Manning BD . Common corruption of the mTOR signaling network in human tumors. Oncogene 2008; 27 (Suppl 2): S43–S51.
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L, Kosmatka M, DePinho RA et al. The LKB1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 91–99.
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A . Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002; 420: 629–635.
Whitehead IP, Campbell S, Rossman KL, Der CJ . Dbl family proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1997; 1332: F1–23.
Erickson JW, Cerione RA . Structural elements, mechanism, and evolutionary convergence of Rho protein-guanine nucleotide exchange factor complexes. Biochemistry 2004; 43: 837–842.
Fritz G, Just I, Kaina B . Rho GTPases are over-expressed in human tumors. Int J Cancer 1999; 81: 682–687.
Schnelzer A, Prechtel D, Knaus U, Dehne K, Gerhard M, Graeff H et al. Rac1 in human breast cancer: overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, Rac1b. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3013–3020.
Kamai T, Arai K, Tsujii T, Honda M, Yoshida K . Overexpression of RhoA mRNA is associated with advanced stage in testicular germ cell tumour. BJU Int 2001; 87: 227–231.
Suwa H, Ohshio G, Imamura T, Watanabe G, Arii S, Imamura M et al. Overexpression of the rhoC gene correlates with progression of ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Br J Cancer 1998; 77: 147–152.
Mira JP, Benard V, Groffen J, Sanders LC, Knaus UG . Endogenous, hyperactive Rac3 controls proliferation of breast cancer cells by a p21-activated kinase-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 185–189.
Fritz G, Brachetti C, Bahlmann F, Schmidt M, Kaina B . Rho GTPases in human breast tumours: expression and mutation analyses and correlation with clinical parameters. Br J Cancer 2002; 87: 635–644.
Kamai T, Yamanishi T, Shirataki H, Takagi K, Asami H, Ito Y et al. Overexpression of RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 GTPases is associated with progression in testicular cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 4799–4805.
Kleer CG, van Golen KL, Zhang Y, Wu ZF, Rubin MA, Merajver SD . Characterization of RhoC expression in benign and malignant breast disease: a potential new marker for small breast carcinomas with metastatic ability. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 579–584.
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES, Hynes RO . Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 2000; 406: 532–535.
Burbelo P, Wellstein A, Pestell RG . Altered Rho GTPase signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2004; 84: 43–48.
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, Calogrias D, Szasz AM, Wang ZC et al. A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell 2009; 137: 1032–1046.
Wang JB, Erickson JW, Fuji R, Ramachandran S, Gao P, Dinavahi R et al. Targeting mitochondrial glutaminase activity inhibits oncogenic transformation. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 207–219.
Stirewalt DL, Appelbaum FR, Willman CL, Zager RA, Banker DE . Mevastatin can increase toxicity in primary AMLs exposed to standard therapeutic agents, but statin efficacy is not simply associated with ras hotspot mutations or overexpression. Leuk Res 2003; 27: 133–145.
Alberts AW, MacDonald JS, Till AE, Tobert JA . Lovastatin. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 1989; 7: 89–109.
Haria M, McTavish D . Pravastatin. A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and clinical effectiveness in the management of coronary heart disease. Drugs 1997; 53: 299–336.
Kajinami K, Mabuchi H, Saito Y . NK-104: a novel synthetic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2000; 9: 2653–2661.
Malinowski JM . Atorvastatin: a hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor. Am J Health Syst Pharm 1998; 55: 2253–2267; quiz 2302-2253.
McTaggart F, Buckett L, Davidson R, Holdgate G, McCormick A, Schneck D et al. Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of rosuvastatin, a new 3-hydroxy- 3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor(1). Am J Cardiol 2001; 87: 28–32.
Plosker GL, McTavish D . Simvastatin. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in hypercholesterolaemia. Drugs 1995; 50: 334–363.
Plosker GL, Wagstaff AJ . Fluvastatin: a review of its pharmacology and use in the management of hypercholesterolaemia. Drugs 1996; 51: 433–459.
Bischoff H, Angerbauer R, Bender J, Bischoff E, Faggiotto A, Petzinna D et al. Cerivastatin: pharmacology of a novel synthetic and highly active HMG- CoA reductase inhibitor. Atherosclerosis 1997; 135: 119–130.
Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J . Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 2001; 292: 1160–1164.
Corsini A, Maggi FM, Catapano AL . Pharmacology of competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Pharmacol Res 1995; 31: 9–27.
Bischoff KM, Rodwell VW . Biosynthesis and characterization of (S)-and (R)-3-hydroxy-3- methylglutaryl coenzyme A. Biochem Med Metab Biol 1992; 48: 149–158.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL . A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986; 232: 34–47.
Zhou Z, Rahme E, Pilote L . Are statins created equal? Evidence from randomized trials of pravastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin for cardiovascular disease prevention. Am Heart J 2006; 151: 273–281.
Jones P, Kafonek S, Laurora I, Hunninghake D . Comparative dose efficacy study of atorvastatin versus simvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin, and fluvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia (the CURVES study). Am J Cardiol 1998; 81: 582–587.
Weng TC, Yang YH, Lin SJ, Tai SH . A systematic review and meta-analysis on the therapeutic equivalence of statins. J Clin Pharm Ther 2010; 35: 139–151.
Wong WW, Tan MM, Xia Z, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD, Penn LZ . Cerivastatin triggers tumor-specific apoptosis with higher efficacy than lovastatin. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 2067–2075.
Gauthaman K, Richards M, Wong J, Bongso A . Comparative evaluation of the effects of statins on human stem and cancer cells in vitro. Reprod Biomed Online 2007; 15: 566–581.
Campbell MJ, Esserman LJ, Zhou Y, Shoemaker M, Lobo M, Borman E et al. Breast cancer growth prevention by statins. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 8707–8714.
Chan KK, Oza AM, Siu LL . The statins as anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 10–19.
Katz MS . Therapy insight: potential of statins for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2005; 2: 82–89.
Mason RP, Walter MF, Day CA, Jacob RF . Intermolecular differences of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors contribute to distinct pharmacologic and pleiotropic actions. Am J Cardiol 2005; 96: 11F–23F.
Shitara Y, Sugiyama Y . Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors: drug-drug interactions and interindividual differences in transporter and metabolic enzyme functions. Pharmacol Ther 2006; 112: 71–105.
Goard CA, Mather RG, Vinepal B, Clendening JW, Martirosyan A, Boutros PC et al. Differential interactions between statins and P-glycoprotein: implications for exploiting statins as anticancer agents. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2936–2948.
Martirosyan A, Clendening JW, Goard CA, Penn LZ . Lovastatin induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells and synergizes with doxorubicin: potential therapeutic relevance. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 103.
Feleszko W, Mlynarczuk I, Balkowiec-Iskra EZ, Czajka A, Switaj T, Stoklosa T et al. Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity and attenuates cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in three tumor models in mice. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2044–2052.
Feleszko W, Mlynarczuk I, Olszewska D, Jalili A, Grzela T, Lasek W et al. Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity of doxorubicin in murine melanoma via an apoptosis-dependent mechanism. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 111–118.
Wang W, Collie-Duguid E, Cassidy J . Cerivastatin enhances the cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil on chemosensitive and resistant colorectal cancer cell lines. FEBS Lett 2002; 531: 415–420.
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB . Reversal of chemoresistance and enhancement of apoptosis by statins through down-regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 2008; 75: 907–913.
Fritz G, Brachetti C, Kaina B . Lovastatin causes sensitization of HeLa cells to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis by the abrogation of G2 blockage. Int J Radiat Biol 2003; 79: 601–610.
Nubel T, Damrot J, Roos WP, Kaina B, Fritz G . Lovastatin protects human endothelial cells from killing by ionizing radiation without impairing induction and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 933–939.
Fritz G, Henninger C, Huelsenbeck J . Potential use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) as radioprotective agents. Br Med Bull 2011; 97: 17–26.
Mathew B, Huang Y, Jacobson JR, Berdyshev E, Gerhold LM, Wang T et al. Simvastatin attenuates radiation-INDUCED MURINE lung injury and dysregulated lung gene expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011; 44: 415–422.
Ostrau C, Hulsenbeck J, Herzog M, Schad A, Torzewski M, Lackner KJ et al. Lovastatin attenuates ionizing radiation-induced normal tissue damage in vivo. Radiother Oncol 2009; 92: 492–499.
Katz MS, Minsky BD, Saltz LB, Riedel E, Chessin DB, Guillem JG . Association of statin use with a pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation for rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005; 62: 1363–1370.
Ray KK, Cannon CP . The potential relevance of the multiple lipid-independent (pleiotropic) effects of statins in the management of acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005; 46: 1425–1433.
Stanislaus R, Gilg AG, Singh AK, Singh I . Immunomodulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rats by Lovastatin. Neurosci Lett 2002; 333: 167–170.
Youssef S, Stuve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL, Hur EM et al. The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 2002; 420: 78–84.
Leoni V, Masterman T, Diczfalusy U, De Luca G, Hillert J, Bjorkhem I . Changes in human plasma levels of the brain specific oxysterol 24S-hydroxycholesterol during progression of multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Lett 2002; 331: 163–166.
Locatelli S, Lutjohann D, Schmidt HH, Otto C, Beisiegel U, von Bergmann K . Reduction of plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol (cerebrosterol) levels using high-dosage simvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: evidence that simvastatin affects cholesterol metabolism in the human brain. Arch Neurol 2002; 59: 213–216.
Meier CR, Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME, Schlegel B, Jick H . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of fractures. Jama 2000; 283: 3205–3210.
Wang PS, Solomon DH, Mogun H, Avorn J . HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of hip fractures in elderly patients. Jama 2000; 283: 3211–3216.
Lupattelli G, Scarponi AM, Vaudo G, Siepi D, Roscini AR, Gemelli F et al. Simvastatin increases bone mineral density in hypercholesterolemic postmenopausal women. Metabolism 2004; 53: 744–748.
Abud-Mendoza C, de la Fuente H, Cuevas-Orta E, Baranda L, Cruz-Rizo J, Gonzalez-Amaro R . Therapy with statins in patients with refractory rheumatic diseases: a preliminary study. Lupus 2003; 12: 607–611.
McCarey DW, McInnes IB, Madhok R, Hampson R, Scherbakov O, Ford I et al. Trial of Atorvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis (TARA): double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2004; 363: 2015–2021.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank members of the Penn lab for helpful discussions and critical review of the manuscript. Financial support: This work was undertaken, in part, thanks to funding from the Canada Research Chairs Program (L.Z.P), the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research through funding provided by the Province of Ontario (L.Z.P.), the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation, Ontario Region (L.Z.P.), the Excellence In Radiation Research for the 21st Century Strategic Training Initiative In Health Research from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (J.W.C.), and the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long Term Care. The views expressed do not necessarily reflect those of the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long Term Care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clendening, J., Penn, L. Targeting tumor cell metabolism with statins. Oncogene 31, 4967–4978 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Activation of invasion by oncogenic reprogramming of cholesterol metabolism via increased NPC1 expression and macropinocytosis
Oncogene (2023)
-
Identification of a cholesterol metabolism-related prognostic signature for multiple myeloma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Increased Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Simvastatin Encapsulated PCL-PEG Nanoparticles on Human Breast Cancer Adenocarcinoma Cells
Journal of Cluster Science (2023)
-
Simvastatin Preferentially Targets FLT3/ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Inhibiting MEK/ERK and p38-MAPK Signaling Pathways
Drugs in R&D (2023)
-
Therapeutic targeting of the mevalonate–geranylgeranyl diphosphate pathway with statins overcomes chemotherapy resistance in small cell lung cancer
Nature Cancer (2022)